How to Choose the Right Cable Tray: A Comprehensive Guide for Electrical Installations
Cable trays are indispensable components in modern electrical installations. They streamline the organization, routing, and protection of electrical wiring and cable networks, ensuring safety and longevity while simplifying installation and maintenance. Choosing the right cable tray, such as those offered by BonnGulf, requires careful evaluation of the materials, design, environment, and application to ensure optimal performance and cost efficiency. This guide delves into the intricacies of cable trays, exploring their types, materials, manufacturing methods, installation techniques, and more, to help you make the best decision for your project.
The Role of Cable Trays in Electrical Installations
The primary purpose of cable trays is to protect and support electrical wiring from mechanical damage and environmental hazards. They serve as a structured conduit for routing power, communication, and data cables, ensuring that the cables remain organized, accessible, and shielded from potential harm. Cable trays also enhance safety by reducing the risk of electrical fires and ensuring compliance with electrical standards.
Benefits of Using Cable Trays
Cable trays offer a range of advantages, including:
- Improved Organization: They provide a systematic way to arrange and support cables, reducing clutter and tangling.
- Enhanced Safety: By securely enclosing cables, trays prevent accidents caused by loose wiring.
- Ease of Maintenance: Organized cables make troubleshooting and repairs more efficient.
- Protection from Environmental Hazards: Depending on the design and material, cable trays shield cables from moisture, dust, and mechanical impacts.
- Scalability: Cable trays can accommodate additional cables, making them suitable for expanding installations.
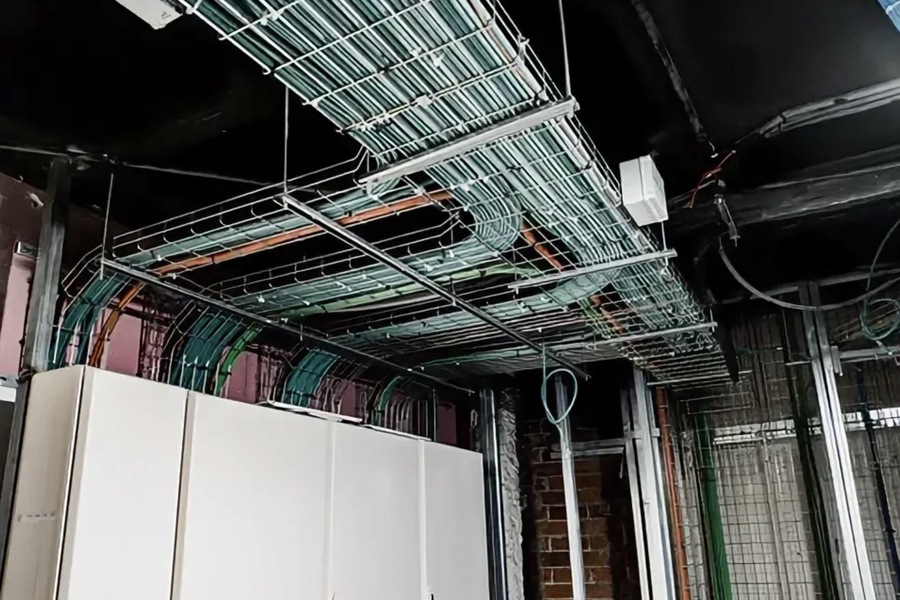

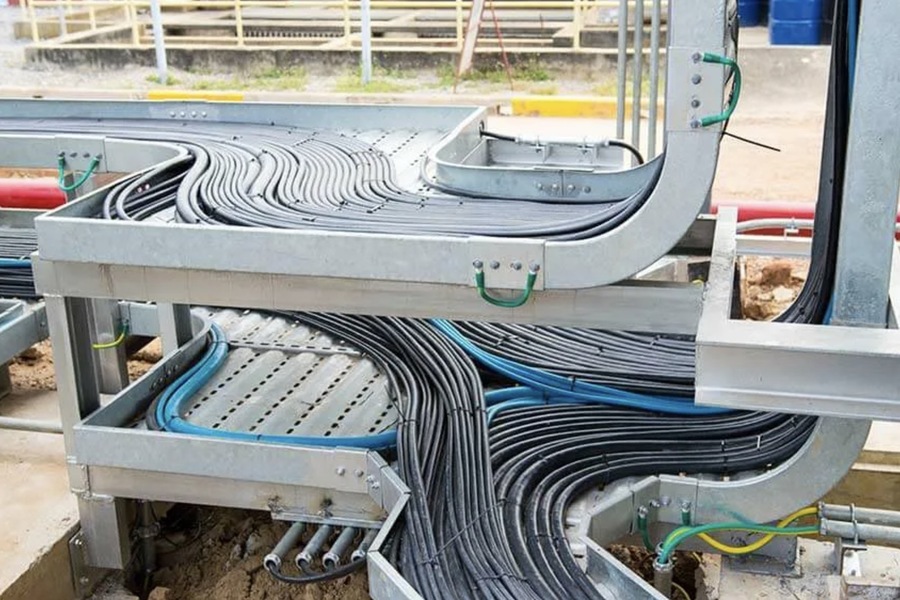
Types of Cable Trays by Design
The design of a cable tray significantly impacts its functionality and suitability for specific environments. Here’s a detailed look at the three primary designs:
- Perforated Cable Trays
Description: Perforated trays feature small holes along their surface, allowing natural ventilation for the cables.
Advantages
→Prevents overheating by promoting airflow.
→Lightweight and easy to install.
→Provides partial protection against dust and debris.
Applications: Suitable for dry indoor environments where humidity is not a concern. Commonly used in commercial buildings and data centers.
Limitations: Vulnerable to moisture and not recommended for outdoor use.
- Wire Cable Trays
Description: These trays are constructed as grid-like structures, resembling a basket or wireframe.
Advantages
→Excellent for lightweight cables.
→Cost-effective for smaller installations.
Applications: Ideal for supporting low-voltage wiring or telecommunications cables in well-ventilated, controlled environments.
Limitations: Offers minimal protection against environmental factors like dust, water, or impact.
- Solid Cable Trays
Description: Solid trays are fully enclosed, providing a sealed environment for cables.
Advantages
→Maximum protection from external elements, including moisture, dust, and mechanical damage.
→Supports heavy-duty applications.
Applications: Widely used in harsh environments, such as manufacturing plants, outdoor installations, and underground cable routes.
Limitations: Lack of ventilation may lead to cable overheating in high-power installations if cooling systems are not integrated.
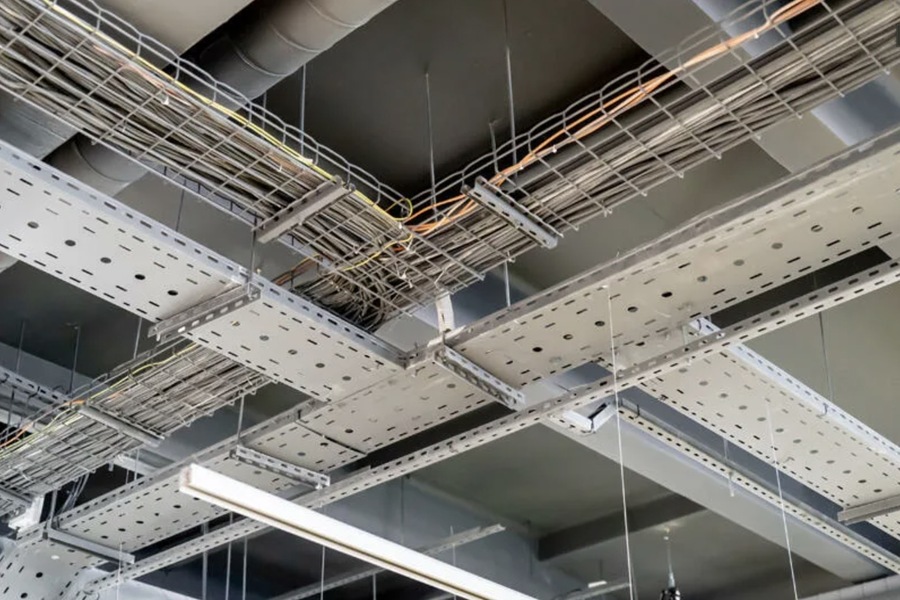

Types of Cable Trays by Manufacturing Method
Cable trays can also be categorized based on their manufacturing techniques, which influence their cost, durability, and suitability:
- Rolled Trays
Manufacturing Process: Made using a rolling process where metal sheets are bent and shaped into U-shaped profiles.
Advantages
→Cost-effective and simple to produce.
→Available in a variety of sizes and thicknesses.
Applications: Ideal for budget-conscious projects in non-corrosive indoor environments.
- Staircase Trays
Manufacturing Process: Side elements are stamped to create a ladder-like design, allowing natural ventilation and robust support.
Advantages
→Strong and durable, capable of supporting heavy cables.
→Facilitates cooling by allowing air circulation.
Applications: Commonly used in industrial environments for power distribution cables.
- Enamel-Coated Trays
Manufacturing Process: Metal trays are coated with enamel to enhance their aesthetic appeal and provide minor protection against corrosion.
Advantages
Attractive finish for installations in visible areas.
Limitations
→The coating offers limited protection and is unsuitable for highly corrosive environments.
Applications: Decorative indoor installations where appearance matters.
Materials for Cable Trays
The material of a cable tray determines its strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and cost. Here are the most common options:
- Plastic Trays
Characteristics: Lightweight and made from PVC or similar materials.
Advantages
→Affordable and easy to handle.
→Resistant to corrosion and suitable for indoor use.
→Flexible, making them ideal for complex routing.
Disadvantages
→Low durability and strength.
→Vulnerable to high temperatures and unsuitable for outdoor installations.
Applications: Telecommunication systems, light-duty indoor wiring.
- Reinforced Concrete Trays
Characteristics: Made from concrete reinforced with steel or asbestos.
Advantages
→Exceptional durability and resistance to wear and tear.
→Withstands heavy loads and adverse weather conditions.
Disadvantages
→Heavy and challenging to install.
→Limited flexibility for routing.
Applications: Underground cable installations, large substations, and industrial projects.
- Metal Trays
Characteristics: Typically made from steel, aluminum, or stainless steel.
Advantages
→High strength and resistance to mechanical damage.
→Can be treated with corrosion-resistant coatings.
Disadvantages
Susceptible to rust without proper treatment.
Applications: Suitable for both indoor and outdoor installations, industrial facilities, and power plants.
Installation Methods
Cable trays are installed using various fastening techniques based on the type of material and surface:
- Self-Tapping Screws: Ideal for wooden surfaces.
- Dowel Nails: Suitable for concrete walls.
- Bug Screws: Used for thin metal surfaces (up to 2 mm).
- Mounting Glue: A versatile but lightweight option, mainly for plastic trays on tiled surfaces.
Criteria for Selecting the Right Cable Tray
When choosing a cable tray, consider the following factors:
- Installation Environment: Indoor or outdoor, temperature, humidity, and exposure to corrosive elements.
- Cable Type: Voltage levels, insulation type, and load requirements.
- Load Capacity: The tray must support the combined weight of all cables and accessories.
- Ventilation Needs: Choose perforated or wire trays for areas requiring natural cooling.
- Aesthetic Considerations: For visible installations, opt for enamel-coated or neatly designed trays.
- Supplier Reliability: Always purchase from trusted manufacturers to ensure quality.
The Trusted Supplier: BonnGulf
In the UAE, BonnGulf is a leading manufacturer of cable trays and accessories. BonnGulf offers high-quality, government-approved systems that cater to the diverse needs of industries ranging from construction to telecommunications. Their extensive product range includes perforated, solid, and ladder trays, all designed to meet international standards.
Conclusion
Choosing the right cable tray is vital for the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your electrical installation. By understanding the various types, materials, designs, and installation methods, you can ensure your project is optimized for current and future needs. Whether for industrial facilities, commercial buildings, or residential setups, selecting a reliable supplier like BonnGulf guarantees quality and compliance with industry standards. With the right cable tray, your electrical systems will remain secure, organized, and resilient against environmental challenges.
Hockey fan, ramen eater, hiphop head, Mad Men fan and RISD grad. Performing at the nexus of minimalism and purpose to craft experiences both online and in real life. I’m a designer and this is my work.